- BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centres provide some assurance of purity and customer confidence in the purchase of gold and silver jewellery.
- These centres are approved by the Bureau of Indian Standards and participate in the Hallmarking Scheme.
- When testing and hallmarking any precious metal, an assaying and hallmarking centre that is BIS recognized must be used by a jeweller.
- If a jeweller sells items with certain levels of purity in India, they must adhere to attention to BIS hallmarking norms, because compliance is a legal requirement!
- This blog will help jewellers with information on how to get in touch with a BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centre and the compliance journey.
Introduction
A case in 2022, a mid-sized jeweller in Ahmedabad, Prakash Jewellers received a customer complaint that the gold was not pure. The jeweller had sold them a 22K piece of jewellery but when the local consumer group tested the jewellery there were inconsistencies in the purity claims. It went viral over social media; their credibility was shaken, and they decided it was time to pay attention to their compliance obligations.
They were back to business rebuilding trust; therefore they registered under the BIS Hallmarking Scheme. They also liaised with a BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centre in Gujarat. In weeks they were able to sell jewellery with the BIS stamp, but most importantly regained customer confidence.
This is not the only story. Jewellers are now seeking compliance with BIS-recognized centres for conformity, credibility and legality of their precious metal products, when compliance becomes mandatory in every state in India.
Understanding the Role of BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centres in Jewellery Certification
The Government of India has recently taken action through the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) to make hallmarking of gold and silver jewellery mandatory. The idea is to protect customers against fraud and promote transparency in selling precious metal articles. A BIS Hallmark is an official mark that confirms the purity or fineness of gold or silver in jewellery or articles of precious metal.
Every item of jewellery with a hallmark has been tested at a BIS Recognised Assaying and Hallmarking Centre which are the only institutions certified by the BIS to test and certify precious articles to the purity claimed by the jeweller. AHCs have the latest testing laboratories and comply with rigorous BIS procedures to ensure they provide accurate information when certifying their jewellery and to retain customer trust.
What are Assaying and Hallmarking Centres (AHCs)?
Assaying and Hallmarking Centres (AHCs) are specialised laboratories recognised by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). Their function is to test individually every jewellery item that is tested from a BIS-registered jeweller to ensure that it complies with the stated purity requirements.
Each AHC is responsible for:
- Testing gold and silver articles for purity
- Certifying gold jewellery in 14K, 18K, and 22K categories
- Certifying 6 purity grades for silver jewellery
- Hallmarking 24K gold coins and medallions
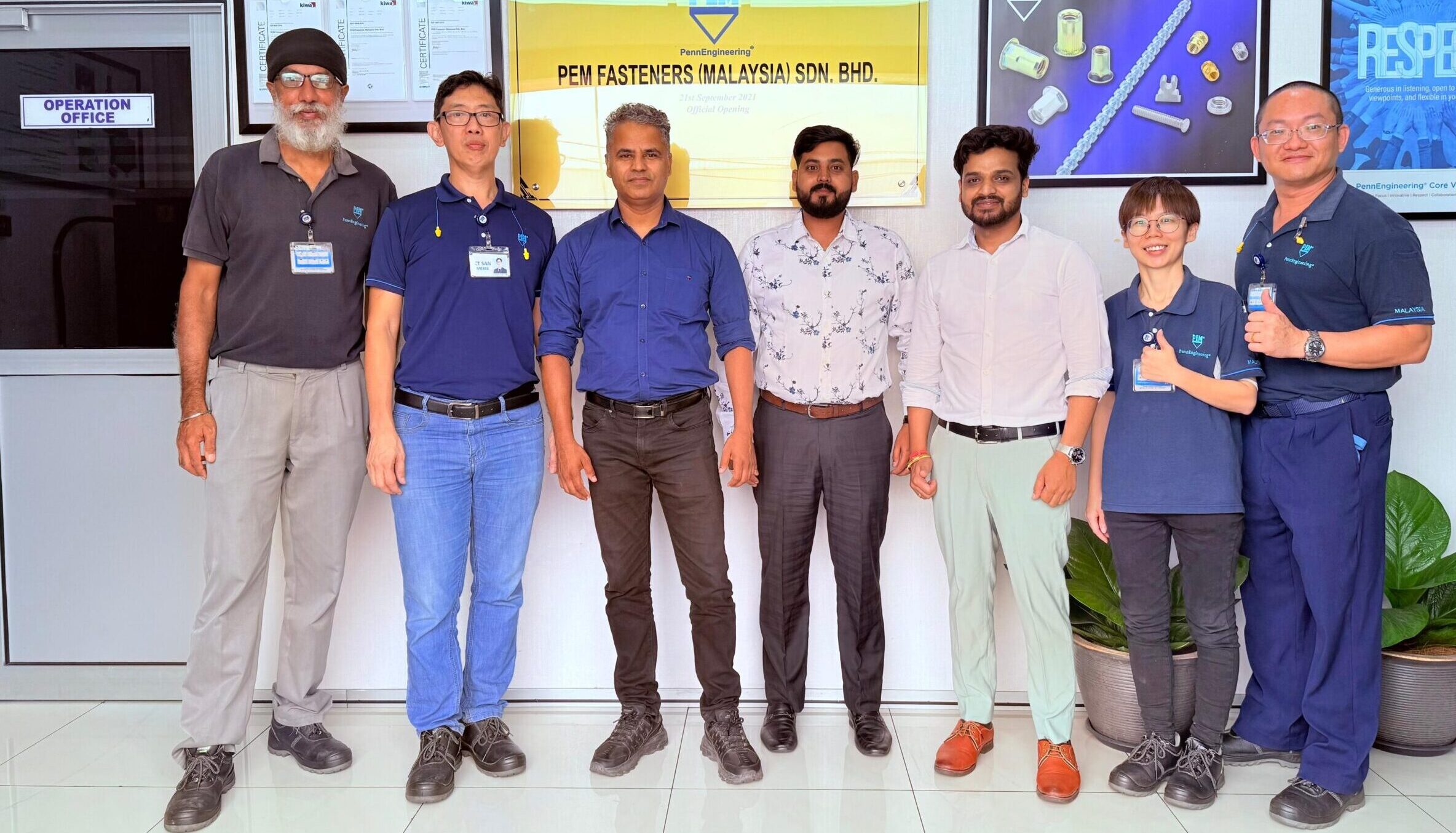
- Assigning the BIS Hallmark, which includes four key marks:
- BIS logo
- Purity grade (e.g., 22K916)
- AHC’s identification number
- Jeweller’s BIS registration number
Once certified by a BIS recognized assaying and hallmarking centre, the article becomes a verified product that can legally be sold under the BIS hallmark registration scheme.
What is a BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centre?

An Assaying and Hallmarking Centre (AHC) recognized by BIS is a laboratory that the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has sanctioned to assay and hallmark gold and silver jewellery in accordance with Indian Standards IS 1417 and IS 2112. AHCs are an integral part of India’s hallmarking ecosystem.
The AHCs conduct scientific assay of precious metals to determine fineness (for example 22K, 18K), and then hallmark the finished product with four key symbols (essentially the jewellery version of the NFL logo):
- BIS logo
- Purity in carat and fineness (for example 22K916)
- AHC identification mark
- Jeweller’s registration number
Think of them as the “ISRO” of the jewellery world—regulated, standardized and trusted.
Why BIS Recognition Matters?
BIS-recognized AHCs aren’t just laboratories—they’re officially licensed to:
- Protect consumers against adulteration.
- Build credibility for jewellers.
- Standardise quality at national and global levels.
If you’re a jeweller selling in India, especially after the mandatory hallmarking notification by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, you must tie up with a BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centre for legal compliance.
Why Leading Jewellery Brands Trust BIS-Recognized Centres
Certified Trust
Leading jewellery brands across India relies on BIS-affiliated Assaying & Hallmarking Centres (AHCs) to verify that every piece of jewellery they sell is certified and pure. This reliance on certified hallmarking is a pillar of consumer trust in Indian consumers.
Efforts Beyond Marketing
The reputation of top jewellery businesses do not fundamentally rely on attractive designs or marketing, but uncompromising quality. Although a BIS hallmark does not guarantee purity, independent certification does lend some level of validation, and contributes to brand legitimacy over the long-run.
Compliance and new marketplaces
Jewellery merchants selling on marketplaces such as Amazon, Flipkart, etc. must comply with BIS Hallmark requirements, like any traditional brick and mortar store. It did not matter if they were a traditional seller or a digital-first offering – all merchants needed to keep consumers informed of their offering by providing hallmarking.
The Role of Assaying and Hallmarking Centres : Ensuring Purity
The importance of AHCs cannot be overstated. With hallmarking becoming mandatory across more districts in India, these centres act as critical intermediaries between jewellers and consumers. When a BIS-registered jeweller submits jewellery for testing, the AHC documents:
- The time and date of receipt
- The nature of the article
- Test procedures and results
- Dispatch details after hallmarking
This structured process allows full traceability of hallmarked products, giving assurance to all stakeholders—jewellers, customers, and regulators.
By maintaining records of every article, AHCs support audit trails and ensure the integrity of the BIS hallmarking scheme.
Why Some Jewellery Cannot Be Hallmarked by AHCs
As much as the hallmarking mandate is conclusive, there are exemptions under which particular jewellery items do not qualify for testing and hallmarked at BIS-recognised assaying and hallmarking centres:
- Items weighing less than 2grams– Articles exempted are either of minimal value or are of low purity.
- Export-oriented items- A piece of jewellery intended for export-only manufacture may be exempt from Indian hallmarking regulations if the foreign buyer specification is met.
- Jewellers with a turnover below ₹40 lakh/year– Small Jewellers in the current norm may exempt from compulsory hallmarking.
- Traditional jewellery made using Polki, Jadau, or Kundan methods- The intricacy of the design made it impossible to hallmark even if no damage occurred during the hallmarking process.
It is essential to grasp the exemptions available to jewellers to avert compliance mistakes and to simplify the process of obtaining the BIS hallmarking process.
Documents Required for BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centre
To obtain recognition as a BIS recognized assaying and hallmarking centre, the following key documents are needed:
- Establishment Proof (any one):
Certificate of Registration with MoA, Registered Partnership Deed, or CA Certificate (for proprietorship). - Address Proof (any one):
GST Certificate, Sale/Lease Deed, Trade License, Property Tax Receipt, or Rent Agreement. - ID Proof:
Aadhar-based e-sign or self-attested ID (Aadhar, PAN, Passport, etc.). - Other Documents:
- Map of the premises
- Affidavit-cum-undertaking
- Quality Manual as per BIS format
Hallmarking Procedure for Recognition
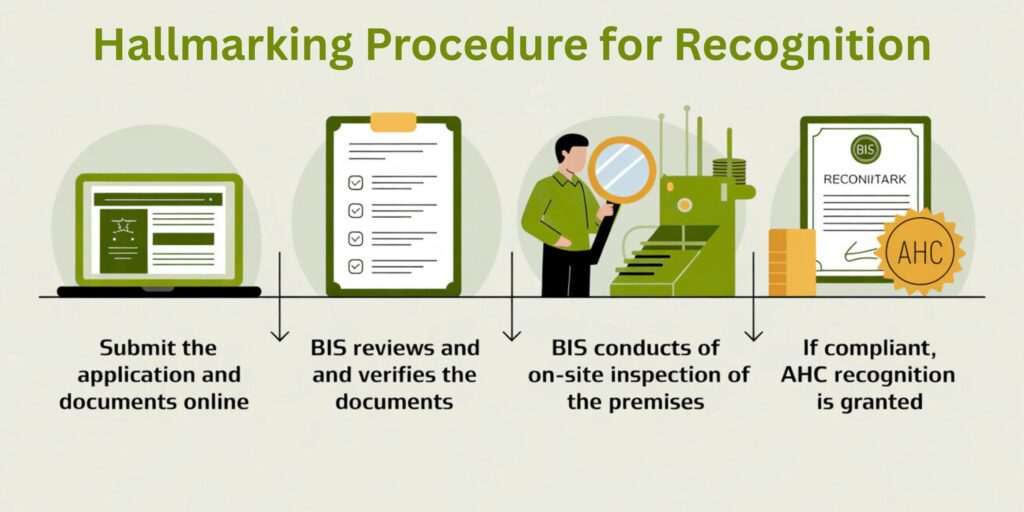
- Submit the application and documents online.
- BIS reviews and verifies the documents.
- BIS conducts on-site inspection of the premises.
- If compliant, AHC recognition is granted under the BIS hallmarking scheme.
Functions of BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centres
- Assaying (testing) the purity of gold and silver alloys
- Marking jewellery with BIS Hallmark symbols
- Maintaining test records and samples
- Ensuring compliance with IS 15820 (for AHC operations)
Legal Framework for Assaying & Hallmarking Centres
BIS-recognized centres operate under:
- BIS Act, 2016
- BIS Hallmarking of Gold Jewellery Order, 2020
- IS 15820: Guidelines for AHC operations
- Ministry of Consumer Affairs notifications
According to BIS over 1,200 BIS-recognized AHCs operate in India as of 2024, ensuring national coverage and convenience for jewellers.
How to Get Jewellery Hallmarked at a BIS Recognized Centre
- Jeweller Must Be BIS Registered: First, jewellers must register with BIS.
- Submit Jewellery to AHC: Items are submitted for testing and hallmarking.
- Assaying: The centre tests for purity and composition.
- Stamping: Jewellery is hallmarked using laser/impression marks.
- Collection: Jeweller receives certified products, ready for sale.
Eligibility Criteria for Becoming a BIS AHC
To become a BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centre, an entity must:
- Be a legally established business
- Have a minimum 1000 sq. ft. lab space
- Possess testing equipment like Fire Assay, XRF, Spectrometer
- Employ qualified staff (Metallurgists, Chemists, etc.)
- Maintain SOPs and calibration standards
- Undergo pre-approval inspections by BIS
Benefits of Using BIS Recognized Assaying and Hallmarking Centres
| Benefit | Description |
| Legal Compliance | Mandatory under government rules |
| Quality Assurance | Verifies gold/silver purity |
| Customer Trust | BIS mark boosts buyer confidence |
| Export Credibility | Accepted in global markets |
| Brand Reputation | Professionalism attracts premium clients |
Conclusion
The current regulated jewellery marketplace requires you to test your gold and/or silver at a BIS recognized assaying and hallmarking centre, it is no longer optional but rather law. Whether a small sole trader, large retail chain or home jeweller, being registered for a BIS mark will assure your customers of the purity of their jewellery is verified and traceable.
These centres function as the technical foundation of India’s hallmarking ecosystem, operating under strict levels of quality control and scientific rigor to confirm that every hallmark item produced meets its claims of caratage whether it is from 22K gold or fine silver. The advantages of being a client of a BIS recognized AHC are multitude: from compliance, credibility, and long term customer trust—please contact us for any distortion questions!
If you are looking to set up, or partner with, an Assaying and Hallmarking Centre, or require assistance in dealing with your BIS hallmarking registration, having professional assistance is critical.
At Diligence Certifications we help jewellers, entrepreneurs and testing labs to work through the BIS approval process from end to end whether this is paperwork, being inspection ready or preparing their quality manual.
Contact our experts today so your jewellery business can be assured that they are meeting all the BIS hallmarking requirements and staying relevant in increasingly
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Omnibus Technical Regulation?
A BIS Quality Control Order (2024) mandating mandatory BIS certification under Scheme‑X for a wide range of machinery/electrical equipment before manufacture, import, sale in India.
When does it take effect?
Enforcement is from 28 August 2025, with an extended deadline of 1 September 2026 for textile‑related machinery.
Which products are covered?
Pumps, compressors, textile looms, cranes, metal‑cutters, generators, switchgear, transformers (refer full HS‑codes in legislation).
What standards must compliance meet?
General design (IS 16819/ISO 12100), Type‑B product categories, and detailed Type‑C standards—whichever applicable, with Type‑C overriding conflicts.
Who needs certification?
Domestic and foreign manufacturers/importers unless exempt (exports, other QCOs, CMVR-governed products).
What is BIS Scheme‑X?
High‑risk industrial certification scheme with rigorous audits, testing, and licensing under BIS.
Steps to get certified?
Identify product, map standards, register in Manakonline, submit dossier, undergo factory audit/test, obtain BIS license or CoC.
What are the exemptions?
Construction machines under CMVR, exports, items covered by other QCOs.
What if non‑compliant?
Prohibition on manufacture/sale/import; BIS may seize non‑certified machinery; possible penalties and business disruption.
How long for compliance?
Domestic compliance takes ~90 days; foreign manufacturers need up to 6–12 months—hence early action critical.



 BIS Certification
BIS Certification
 CDSCO
CDSCO
 CPCB
CPCB
 LMPC
LMPC
 WPC Approval
WPC Approval
 Global Approvals
Global Approvals
 TEC
TEC
 ARAI
ARAI
 BEE
BEE
 ISO Certification
ISO Certification
 DGCA Certification
DGCA Certification
 NOC For Steel
NOC For Steel
 APEDA Registration
APEDA Registration



















 Business Registration
Business Registration
 FSSAI Mark Certification
FSSAI Mark Certification













 Legal Services
Legal Services
 Trademark Registration
Trademark Registration
 Copyright Registration
Copyright Registration
 Patent Registration
Patent Registration

















































