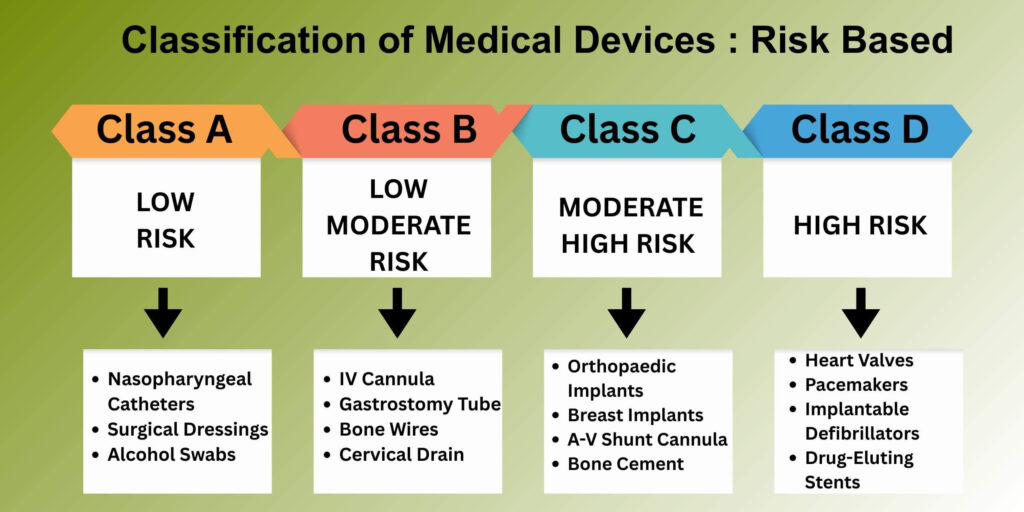
- Classification of Medical devices is done based on risk: A (low risk), B (low-moderate), C (moderate-high), D (high risk).
- Different and correct classification with CDSCO is very important, and provides assurance with regulatory compliance, and will provide honest advice with medical devices registration.
- Includes: online submission to CDSCO portal; submission of technical dossier; conduct of clinical evaluation (Class C & D devices); management of post-approval amendments.
- Includes critical medical devices which includes cardiac stents, IV cannualas, orthopaedic implants, pacemakers, breast implants indicating real business as it relates to implementing and/or overlap of CDSCO rules.
- A correct medical device classification can establish patient safety, expedite approvals, satisfy legal.
Introduction
In 2018, a leading medical technology company based in Delhi confronted a series of timeline delays for its insulin delivery system to be introduced to the market. Although the delivery system received every credentialing certification imaginable internationally, the introduction of the delivery system in India had stalled due to the misclassification of a medical device under the CDSCO timeframes and classification levels.
This is an example of a problem common to med-tech innovators; if one does not understand classification, the compliance actions become an hard burden filled with timelines, distance, costly expenses in introducing a market, ultimately hoping for an approved device or registration.
It is necessary to have a complete understanding of CDSCO’s regulatory and device classification system. It is not only important for getting approval as a innovation , but also for aligning with a safety standard internationally, which further mitigates one’s risk and enhances patient safety.
Overview of CDSCO and India’s Medical Device Regulations

The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) functions under the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI), managing the regulation and classification of medical devices.
India’s medical devices framework relies on:
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940
- Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945
To strengthen compliance, the Medical Devices Rules, 2017 were implemented on 1st January 2018. These rules aim to:
- Reduce the need for frequent license renewals
- Introduce online submission and tracking through the CDSCO portal
- Align India’s regulations with international standards
- Empower the National Medical Device Authority to oversee safety, price control, and quality compliance
Key Features of the Medical Devices Rules, 2017
Streamlined Licensing for Continuous Operations
- Explains how the new rules eliminate annual renewals, keeping licenses valid until suspended, revoked, or surrendered.
- Highlights how this reduces administrative delays and accelerates market access.
CDSCO Portal – Simplifying Cdsco Registration and Compliance
- Details online submission, tracking, and communication with CDSCO.
- Covers Post-Approval Change (PAC) management for device modifications.
- Provides real-world examples of manufacturers benefiting from digital compliance.
Alignment with Global Standards for Risk-Based Classification
- Shows how India now follows GHTF guidelines for classification of medical devices.
- Explains the impact on international compliance, exports, and patient safety.
- Highlights enhanced monitoring requirements for moderate- and high-risk devices (Classes C & D).
CDSCO Classification of Medical Devices
India classifies medical devices into four risk-based categories:
| Class | Risk Level | Examples |
| A | Low | Surgical dressing, nasopharyngeal catheters |
| B | Low-Moderate | IV cannulae, insulin pen needles, bone wires |
| C | Moderate-High | Coronary stents, orthopaedic implants, breast implants |
| D | High | Heart valves, pacemakers, implantable defibrillators |
“Risk-based classification under CDSCO ensures patient safety while guiding manufacturers through the compliance journey.”
Regulatory Authority for Each Class
- Class A & B: Managed primarily by State Licensing Authorities for production and import.
- Class B, C & D: CDSCO handles central-level approval for high-risk and life-saving devices.
Ensure risk-appropriate ISO 13485 certification, technical documentation, and, for Class C/D, clinical evaluation data.
CDSCO Classification of Medical Devices
Class A – Low Risk
| Device | Example Use |
| Nasopharyngeal Catheters | Clear nasal airway obstructions |
| Surgical Dressings | Non-adherent pads, periodontal kits |
| Alcohol Swabs | Sterilising injection sites |
| Umbilical Occlusion Devices | Stop neonatal blood flow temporarily |
Class A devices are low-risk, non-invasive, and require minimal compliance. State authorities can grant licenses quickly.
Class B – Low-Moderate Risk
| Device | Example Use |
| Fibreoptic Oximeter Catheter | Monitor oxygen consumption |
| IV Cannula | Deliver drugs, fluids, or blood |
| Insulin Pen Needles | Safe insulin administration |
| Gastrostomy Tube | Supply nutrition to the stomach |
| Bone Wires | Stabilise fractured bones |
| Cervical Drain | Prevent postoperative complications |
Class B devices are slightly more invasive, requiring state-level registration with risk-based audits.
A Mumbai start-up producing insulin needles obtained swift state approval for Class B devices, allowing nationwide distribution within three months.
Class C – Moderate-High Risk
| Device | Example Use |
| Bifurcation Cardiac Stent | Improve arterial side branches |
| Vein Ablation Device | Treat varicose veins |
| Orthopaedic Implants | Replace missing bone or joint segments |
| Breast Implants | Cosmetic or reconstructive augmentation |
| A-V Shunt Cannula | Facilitate repeated hemodialysis |
| Bone Cement | Fix prosthetic implants to bone |
Class C devices require clinical evaluation, risk analysis, and CDSCO approval.
Class C devices are like “critical bridge structures” in healthcare—slight errors can have major consequences, so the regulatory scrutiny is high.
Class D – High Risk
| Device | Example Use |
| Heart Valves | Regulate blood flow in the heart |
| Pacemakers | Regulate cardiac rhythm |
| Implantable Defibrillators | Correct life-threatening arrhythmias |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | Prevent arterial blockage post-stent placement |
These devices are life-saving and require rigorous clinical trials, documentation, and ISO-compliant manufacturing audits. CDSCO may conduct pre-market inspections before approval.
Importance of Accurate Classification of Medical Devices
Accurate classification of medical devices under CDSCO is crucial for manufacturers/operators. The main benefits are:
- Correct classification of medical devices under Cdsco facilitates compliance with Medical Devices Rules, 2017 and prevents penalties and refunds.
- Increased efficiency around registration with medical devices and decreasing the time for Cdsco Registration.
- It is necessary to properly classify the devices to ensure that they are up to industry standards to ensure the safety of the patient/user and also to ensure integrity of the marketplace and enhance trust.
CDSCO Registration Process – Step-by-Step Guide
Medical devices registration is undergo a systematic risk-based registration process. Following the steps below will help in maintaining compliance and minimizing delays in approval:
Step 1: Identify the Device Classification
- Determine the risk classification (A, B, C, or D) for your device based on duration of use, and its impact to patients.
- Be sure to use CDSCO’s official guidelines to confirm the classification.
Step 2: Compile Required Documentation
For all devices, you will need to collect the following documentation:
- Manufacturer credentials and ISO 13485 certification
- Technical specifications, design features, and any safety studies
- Clinical evaluation reports (a requirement for Class C and D devices)
- Documentation of risk analysis
Step 3: Submit your Application
- The CDSCO portal will allow you to access the online application. You will complete all requested forms and upload required documentation.
- You will also be able to track the status of your application through the Sugam portal and have automated communication with CDSCO.
Step 4: Post approval Change (If applicable)
- If you require changes after the approval process (for example: updates to materials, minor design changes) you will now access the Post Approval Change (PAC) facility within the CDSCO portal.
- Submit your rationale with supporting documentation for review.
Step 5: Inspection and Verification of Compliance
- For Class C and D devices, CDSCO has the authority to conduct pre-marketing inspections of the manufacturing site.
- These audits are designed to ensure quality compliance, the integrity of your clinical data, and compliance with the condition of safe manufacture.
Step 6: Approval & License
The production or import license is issued once the CDSCO or State Licensing Authority assesses compliance with the applicable rules. Licenses remain valid until suspended, revoked, or surrendered.
Timeline and Cost for Classification and Registration of Medical Devices
The timeline and cost is important for manufacturers and importers seeking to register with Cdsco.
Timeline for CDSCO Registration
- Class A/B (Low to Low-Moderate Risk): 30–60 days for approval at the state level.
- Class C/D (Moderate to High-Moderate Risk): 6–12 months including clinical evaluation, audits, and CDSCO approval at the central level.
- Post-Approval Changes (PAC): 2–4 weeks for minor modifications to any approved medical device, subsequently submitting to the Sugam portal.
Cost of Registration
- Application Fees: Fees are established by CDSCO by class and type of device. Low-risk devices may incur a nominal application fee, but high-risk devices may incur a higher application fee.
- Documentation & Compliance: ISO13485 certification, Clinical Trials (for Class C/D), risk assessment, and testing.
- Consultancy & Expert Support: Optional, but recommended for a smooth medical devices accountable registration and compliance process.
Pro Tip: Correctly classifying medical devices and having all completed documentation frequently reduces approval timelines and costs closures.
Conclusion
The classification of medical devices under the CDSCO is critical for compliance, patient safety, and market access. India’s 2017 Medical Devices Rules and the CDSCO portal have provided easy licensing, harmonized regulations with global standards, and improved public safety.
- The manufacturers and importers need to focus on their classification of medical devices accurately
- the full documentation of the medical devices registering
- the compliance to a quality system based on ISO
- proactive communication to the CDSCO
These best practices, together with the CDSCO rules, will support medical device companies to successfully operating in India’s regulatory environment whilst providing for patient safety and market access.
Contact our team at Diligence Certifications if you require detailed compliance assistance in respect of CDSCO classification and registration, and to ensure your devices are compliant. Diligence Certifications offers no nonsense compliance assistance, and will support you to obtain regulatory approvals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the classification of a medical device by the CDSCO?
Classification is based on risk, and the devices are categorized as Class A (low-risk) to D (high-risk) to support the registration of medical devices.
How does the class relate to the registration process?
Class A/B medical devices can be registered through State Licensing Authority Approval. Class C/D medical devices can be registered through central CDSCO approval.
Can a classification change for a device?
Yes, based on new clinical data and/or safety updates as reported through the Sugam portal.
What information/documents are required for the registration of a high-risk device?
Technical specifications, ISO 13485 certification, clinical evaluation reports, and an analysis of the risks associated with the device.
How long is the registration process?
Class A/B medical devices: 30-60 days; Class C/D medical devices: 6-12 months. Being cognizant of what the classification is of the medical device(s) can facilitate the registration process.







 BIS Certification
BIS Certification
 CDSCO
CDSCO
 CPCB
CPCB
 LMPC
LMPC
 WPC Approval
WPC Approval
 Global Approvals
Global Approvals
 TEC
TEC
 ARAI
ARAI
 BEE
BEE
 ISO Certification
ISO Certification
 Drone Registration
Drone Registration
 NOC For Steel
NOC For Steel



















 Business Registration
Business Registration














 Legal Services
Legal Services
 Trademark Registration
Trademark Registration
 Copyright Registration
Copyright Registration
 Patent Registration
Patent Registration
















































