- Purpose: Convert electric energy from one form to another, either from AC to DC or vice versa, or between different levels of voltage using semiconductor devices.
- Types: Rectifies (AC-DC), Inverter (DC-AC), Chopper (DC-DC), Cycloconverters (AC-AC).
- Main Components: Uses devices such as diodes, thyristors, IGBTs, and MOSFETs.
- Application: Used in EVs, solar systems, motor drives, and power supplies.
- Control: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is typically used for efficient output control.
Introduction
Power semiconductor converters are the heart and lungs for energy electronics in power systems involved in efficient and effective energy conversion and control. These devices find their applications as building blocks in industrial and consumer appliances, systems, and renewable energy applications, where they must be qualified and made safe — hence encouraging BIS Compliance.
In India, the Bureau of Indian Standards is making compulsory Scheme X certification for various types of power semiconductor converters and their assemblies, subassemblies, and components. This blog thus covers all the ins and outs, ranging from types of power semiconductor converters to the nature of the BIS certification, documentation, and compliance requirements.
Power semiconductor converters
Power semiconductor converters, also called as power semiconductor converters are electronic devices that render various changes and control electrical energy from one source to another by utilizing semiconductor components such as diode, thyristor, IGBT, and MOSFET. The fields that usually use these devices are Power supplies, Electric vehicles, Industrial automation, Renewable energy systems, Consumer Electronics, Rail traction systems, Data centers and UPS systems.
Apart from converting voltage, modifying frequency, and transforming current, converters form part of the ‘brain’ and ‘muscle’ of an electrical system. Being so widely used, a fault could impact and touch quite a few areas and make it cross-trader – possible for damages – thus, safety compliance takes extreme importance.
– Power Source Converters
– Electric Mobility
– Industrial Automation
– Renewable Power Systems
– Consumer Electronics
– Rail systems
– Commercial Centers and UPS systems
– Act as “brain and muscle” for any electrically powered system that transforms voltages, modifies frequencies, or transforms currents. Given their widespread applications, faults have very far-reaching implications and thus make safety standards compliance a prerequisite.
Types of Power Semiconductor Converters

Understanding the types of converters is key to identifying their certification category. Here are the major types:
1. AC-DC converters also called rectifiers are devices that convert alternating current into direct current and find wide applications in power supplies, battery chargers, and DC motor drives.
2. DC-AC converters change the current again, that is, they convert direct current to alternating current. They find application in solar inverters, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and electric vehicles.
3. DC to DC Converters (Choppers)
These change the voltage level of a DC power source. Common applications include battery management systems, LED drivers, and mobile chargers.
4. AC to AC Converters (Cycloconverters & Matrix Converters)
These modify the frequency or voltage of AC supply and are often used in variable-speed motor drives.
5. Hybrid Converters / Modular Converters
These integrate different types of converters for advanced applications such as smart grids, electric vehicles, and high-performance computing.
Power Semiconductor Modules and Parts Covered Under BIS
BIS does not only regulate final products but also covers crucial sub-assemblies and components that are integral to the performance and safety of the converter. These may include:
- Semiconductor switches (IGBTs, MOSFETs, Thyristors)
- Gate driver circuits
- Control boards and microcontroller units
- Power modules and brick assemblies
- Capacitor banks and snubber circuits
- Cooling mechanisms such as heat sinks and fans
- Input/output filter circuits
All these components, when critical to end-use safety and electromagnetic performance, may fall under BIS certification either individually or as part of an assembly.
BIS Compliance for Power Semiconductor Converters
To ensure product safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and consistent performance, the BIS mandates that power semiconductor converters and their assemblies conform to relevant Indian Standards (IS). Some of the common standards applicable include:
- IS 16242 (Part 1): Safety of power converters for use in photovoltaic power systems
- IS 13252 (Part 1): General safety requirements for information technology equipment
- IS 616: Audio, video and similar electronic apparatus – Safety requirements
- IS 17087: Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards for industrial environments
BIS categorizes these products under Scheme X, which involves rigorous testing and factory audits to verify conformance to standards.
BIS Certification Process (Scheme X)
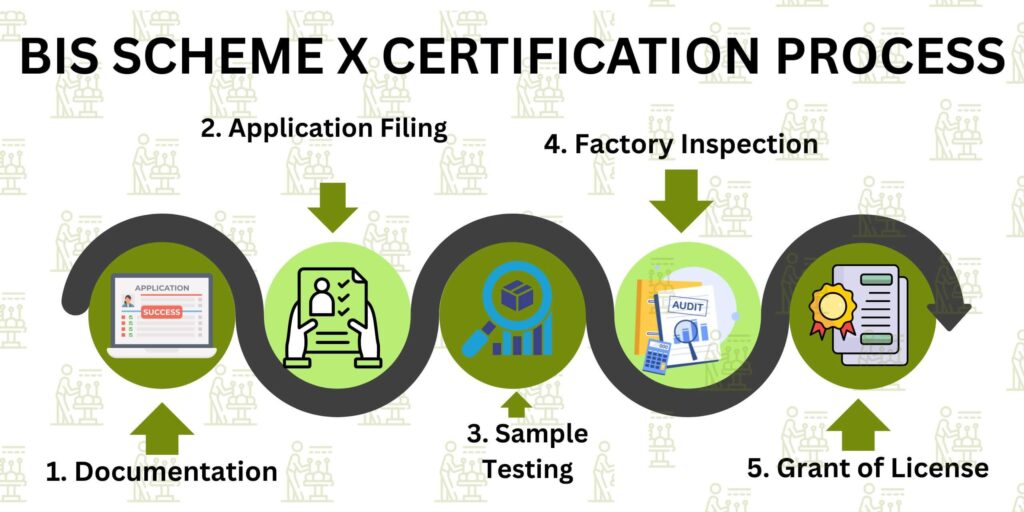
Here’s how the BIS Scheme X certification process typically works:
1. Determine Applicability
The first step is identifying whether your product falls under the compulsory certification list. This can be done by reviewing BIS notifications and consulting with compliance experts.
2. Select Applicable Standards
Every type of power converter must conform to specific Indian Standards. It’s essential to correctly identify the standard to avoid delays.
3. Documentation
Proper documentation is key. Typical documents required include:
- Product specifications and circuit diagrams
- Bill of materials
- Safety test reports
- Manufacturing process flow chart
- Quality control plan
- Factory location and license details
4. Application Filing
The application is submitted through the BIS portal with all supporting documents. Fees are paid at this stage.
5. Sample Testing
The product samples are sent to BIS-recognized laboratories for safety and EMC testing. Only BIS-accredited labs are authorized for testing.
6. Factory Inspection
For most products under Scheme X, BIS officials will conduct a factory audit to inspect the quality control system and manufacturing setup.
7. Grant of License
In case the product and factory satisfy the codes, a certification license would be issued by BIS, which enables the manufacturer to put the Standard Mark- ISI mark on his products.
Role of Authorized Indian Representative (AIR) for Foreign Manufacturers
If you, as a foreign manufacturer, intend to sell power semiconductor converters or power semiconductor assemblies in Indian territory, you will have to appoint an Authorized Indian Representative (AIR) in your sole capacity as a representative in India. The AIR serves as the interface between the manufacturer and the BIS.
The responsibilities of the AIR include:
- Submitting the BIS application on behalf of the manufacturer
- Coordinating product testing and documentation
- Facilitating communication with BIS
- Ensuring post-certification compliance
At Diligence Certification, we act as the AIR for several global brands to ensure smooth BIS certification for their semiconductor and power electronic products.
Why BIS Certification Matters for Power Semiconductor Products
Acquiring BIS certification for your semiconductor converters and modules is more than a government law; it is an advantage in your overall development strategy. Here are the reasons why:
1. Compliance with Internal Law
In India, some electronics must acquire BIS certification. The consequences of failure in compliance are detrimental to the product itself, such as product confiscation, penalties, or a prohibition on import/sale.
2. Access to New Markets
Only products certified by BIS can be marketed in the Indian market. This is a major step towards gaining entry into India’s largest consumer industrial base.
3. Safety and Quality in Products
It ensures that safety and performance standards are met, protects consumers, and improves the image of the brand.
4. Competitive Advantage
Most of the tenders and government orders contain certified products, as do most B2B sales.
5. Local Plus Global Acceptance
Even though BIS is an Indian standard, it is in line with global best practices, thus increasing the credibility of your brand abroad.
Conclusion
Energy-efficient and smart electronics, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, or even industrial drives-highly reliable power semiconductor converters are prime enablers in all these applications. Balancing high safety and reliability has no compromise in such applications.
Power semiconductor converters are the key enablers of energy-efficient and smart electronics. Whether it be electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, or industrial drives, safety and reliability are uncompromising requirements.
Therefore, the Bureau of Indian Standards has made certification of such devices and any critical assembly a must-have.
Types of power semiconductor converters and knowledge of BIS Scheme X certification are pertinent for manufacturers, importers, and distributors alike. Equipped with adequate knowledge and guidance, diligence certification can then be an easy way to ensure quality, build trust on the road, and carve new market opportunities.
Need Help with BIS Certification?
At Diligence Certification, we specialize in BIS registration and compliance consulting for power electronics and semiconductor products. Whether you manufacture in India or abroad, our expert team can guide you from documentation to certification — end to end.
📞 Contact us today to begin your BIS compliance journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is BIS Certification for Power Semiconductor Converters?
BIS Certification ensures that power converters comply with safety, quality, and EMC standards in India under Scheme X.
Is BIS Certification compulsory for power converters in India?
Yes, BIS certification is obligatory for specified categories of power semiconductor converters and their components.
What types of converters will need the BIS certification?
AC to DC (Rectifier), DC to AC (Inverter), DC to DC (Chopper), AC to AC (Cycloconverter), and Hybrid Converters.
What Indian Standards are applicable to power converters?
The following Indian Standards are relevant to power converters (often depending on the application of the product): IS 16242 (part 1), IS 13252, IS 616, IS 17087.
Who needs to apply for BIS Certification?
Manufacturers (domestic manufacturers or foreign manufacturers) wishing to sell a regulated power semiconductor converter in India.
What is Scheme X and the process under BIS?
Scheme X – scheme of type testing, factory audit, and routine surveillance in the case of certified products.
What components does BIS cover?
Components considered critical for the functions of power converters which may require certification include IGBTs, MOSFETs, thyristors, gate drivers, control boards, power modules etc.
How long will the BIS certification process take?
Generally 4 – 8 weeks depending on document readiness, duration for tests, and factory audit.
Do foreign manufacturers need to have a representative in India?
Yes, foreign manufacturers must appoint an Authorised Indian Representative (AIR) who will be responsible for managing the logistics of all procedures regarding BIS locally.
What if I sell non-certified products?
Selling regulated non-certified products can lead to penalties, confiscation of products, or prohibition on the import of products.



 BIS Certification
BIS Certification
 CDSCO
CDSCO
 CPCB
CPCB
 LMPC
LMPC
 WPC Approval
WPC Approval
 Global Approvals
Global Approvals
 TEC
TEC
 ARAI
ARAI
 BEE
BEE
 ISO Certification
ISO Certification
 DGCA Certification
DGCA Certification
 NOC For Steel
NOC For Steel
 APEDA Registration
APEDA Registration



















 Business Registration
Business Registration
 FSSAI Mark Certification
FSSAI Mark Certification













 Legal Services
Legal Services
 Trademark Registration
Trademark Registration
 Copyright Registration
Copyright Registration
 Patent Registration
Patent Registration

















































